Brief description of Y-DNA branches common among Abkhaz-Abaza people.
Haplogroup G2a2
G2a2 plays a major role in the ethnogenesis of the NWC people, it is with them that the origin of Proto-NorthWestern Caucasian languages is associated. Most likely the ancestors of NWC G-L1264 came from Europe (Trypillia culture).
G2a2 (TMRCA 17000) → G-L1264 (TMRCA 4200) → G-S9409 (TMRCA 3700)
Origin: Trypillia culture (?) → PNWC → Proto-Abkhaz-Abaza
A subbranch of subclade G-L1264, which is probably associated with the separation of the Proto-Abkhaz ethnic group and language from the Proto-NorthWestern Caucasian
The most common branch among Abkhazians and Abaza people.
G2a2 (TMRCA 17000) → G-L1264 (TMRCA 4200) → G-Y93425 (TMRCA 2400)
Origin: Trypillia culture (?) → PNWC → ?
The second most common branch in the G-L1264 subclade among the Abkhazians, the most common branch among the Circassians from Abadzekh tribe.
G2a1
Abkhazians and Abaza do not form separate branches in haplogroup G2a1, like all the peoples of the Caucasus, they huddle in small branches, having the most concentration in branch G-FGC750 (TMRCA 4300)
Origin: Zagros → Koban culture → Modern Caucasians
J2a
Abkhazians are characterized by a wide variety of J2a branches.
We will list only the most common ones.
J2a → J-SK1313 (TMRCA 13400) → J-Y26651 (TMRCA 5100)
Origin: CHG → Pre-Caucasians → Western Caucasus
One of three Y branches associated with Caucasian hunter-gatherers (CHG).
The second most common branch among the Abkhazians. Perhaps some of the roots characteristic of all three autochthonous language groups in the Caucasus are some kind of heritage of the CHG language (or more recent language).
Pre-Caucasian (?): -k(ʲ)ʷə (heart)
Proto-NWC: a-ɡ(ʲ)ʷə (heart)
Proto-Kartvelian: ɡuli (heart)
Proto-NEC: -r-kʷə (heart)
J2a → J-M67 (TMRCA 12000) → J-Y30811 (TMRCA 5800)
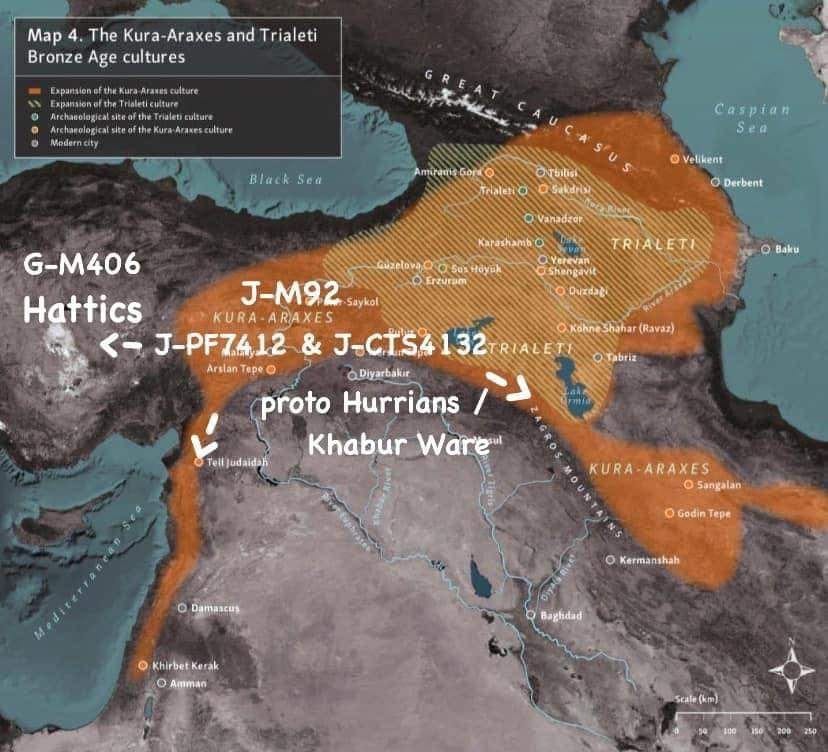
Origin: Anatolia → Maykop culture → Western Caucasus
This subclade is associated with the Maykop culture.
Most common among Abkhazians, Mingrelians, Kabardians and Balkars.
Autosomally Maykopians closest to the modern Mingrelians, perhaps the Kartvelians of Proto-Mingrelian-Zan tribe coming from the south mixed with the Maykopians, who migrating to the south under the pressure of the PNWC G-L1264 People. Although perhaps the truth lies in the fact that the Mingrelians simply were not subject to such Indo-European autosomal influence as the Abkhazians and Circassians, thereby maintaining closeness to the Maykopians.
J2a → J-M67 (TMRCA 12000) → J-M92 (TMRCA 8400)
Origin: Anatolia → Proto-Hurro-Urartian
Abkhazians do not form separate branches in this subclade.
R1a
Among the Abkhazians there is a huge variety of R-Z93 branches, a distinctive feature of this subclade among the Abkhazians is its prevalence among aristocratic clans.
In addition to genetics, connections between the Abkhazians and Scythian-Sarmatians are also confirmed by archeology (Scythian-type burials in Abkhazia) and linguistics (language borrowings from some Scythian language, and from Alanic):
adźa- (goatling) ← *a'ja (goat)
awaraš (beer) ← wæras (mashing)
ara(d)zən (silver) ← *arzatan (silver)
ac̆ə (horse) ← *aśwā (horse)
aśa (sword) ← *aśi (sword)
ajira (herbage) ← *ajra (grassland)
apšʷəma (husband) ← fysym (cattle-owner)
akʼarkʼalaməšʷ (lizard) ← krkālasa (lizard)
amardja (battle-cry) ← *mardjana (destruction)
anəχa (shrine) ← *nikāsa (appear, shine)
Overall more than 100 suggested contact words.
Let's look at the most common and interesting branches.
R-Z93 (TMRCA 4500) → R-Y57 (TMRCA 4300) → R-BY87922 (TMRCA 2900)
Origin: Proto-Indo-Iranians → Sarmatians → Abkhazian nobility
R-Z93 (TMRCA 4500) → R-YP451 (TMRCA 2400) → R-FTB9922 (TMRCA 500)
Origin: Proto-Indo-Iranians → Kipchaks in Georgia (?) → Abkhazian nobility
R-Z93 (TMRCA 4500) → R-Y37912 (TMRCA 3200)
Origin: Proto-Indo-Iranians → Alanians → Abaza
Other haplogroups
R1b
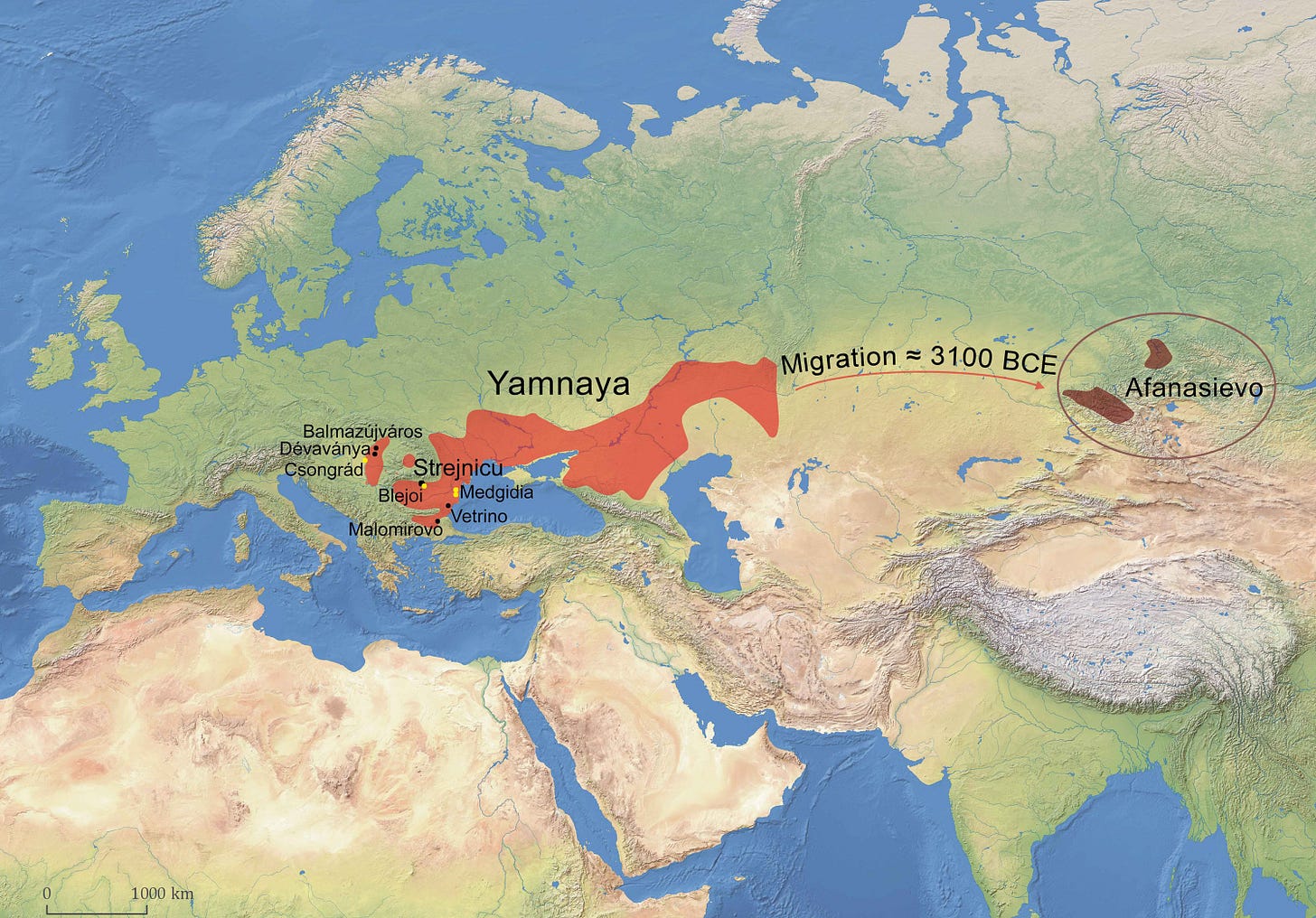
R1b are not grouped among the Abkhazians, being to different migrations, but they are all united by their origin from the Yamnaya culture.
J1
Among the Abkhazians there is also diversity of J1; it is also noteworthy that the Abkhazians are the only ones in the Western Caucasus who have Satsurblia-like J1.
I2
In the Caucasus there are I2a1, I2a2 a I2c, most interesting subclade I-PH2670.
Subclade I-PH2670 is found among a number of Bzyp clans: Bartsits, Kapsh, Khutaba, Blabba, Enik, Kutarba etc. It is interesting that they are all united by the legend of a common descent from three brothers Ecwkjis, Wabyd and Badija. The marker distance among these clans is so great that if these brothers were real people, then most likely they lived more than a thousand years ago.
L1b + J2b
In the Caucasus, both haplogroups are primarily associated with Colchis.